How to Add OAuth2 Authentication to Your MCP SSE Server | Step-by-step Tutorial
Video
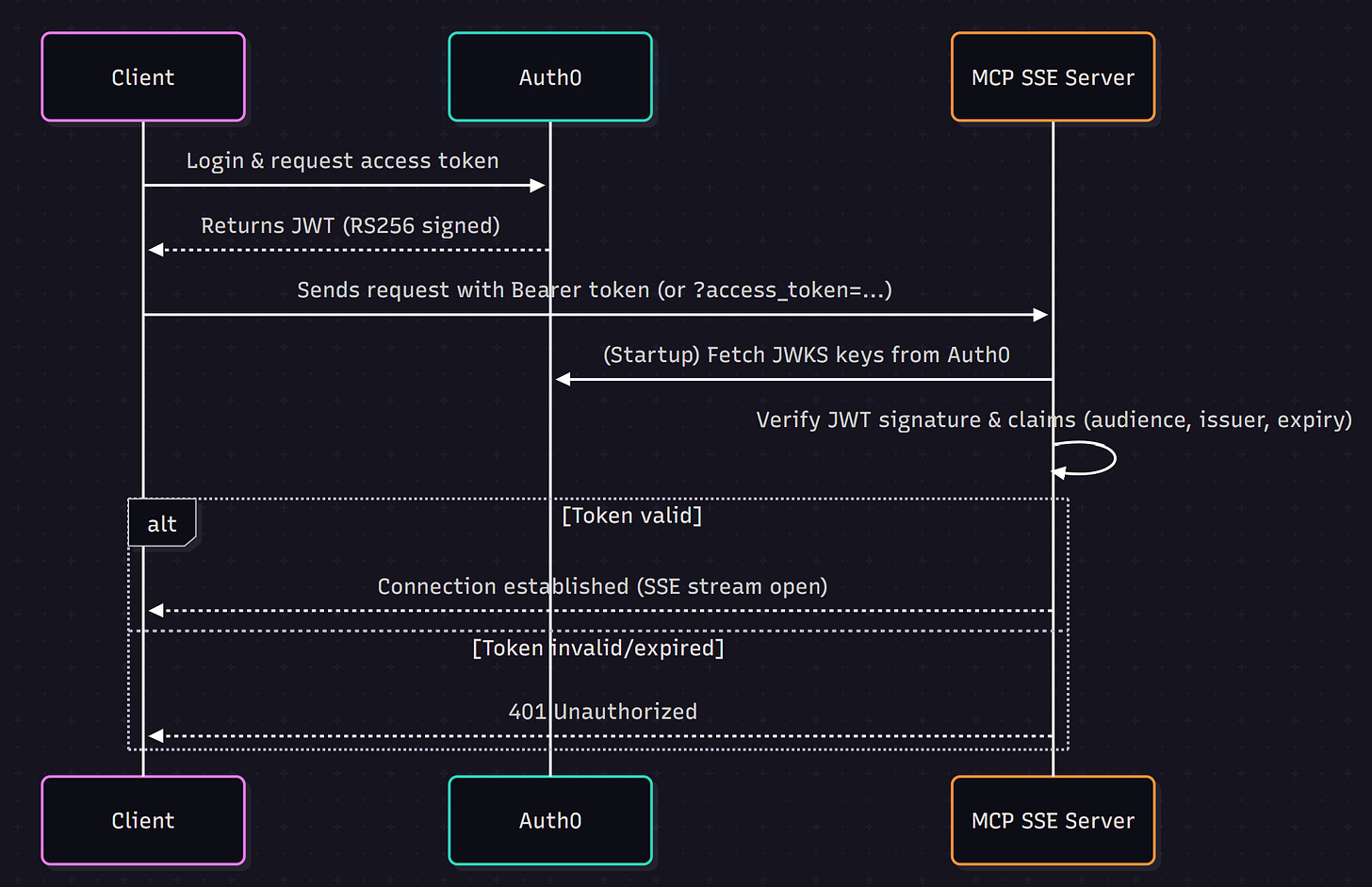
Authentication Flow
Before looking at the code, let’s see how the authentication flow works:
Key points from the flow:
Clients log in via Auth0 and receive a JWT access token.
The server uses Auth0’s JWKS (JSON Web Key Set) to validate token signatures.
Requests without a valid token are rejected with 401 Unauthorized.
Create Auth0 Service (Or any other OAuth provider)
**We are using Auth0 as it is free**
Use your github/google account to signup to Auth0 service
Create a Machine-to-Machine app and generate your domain, client id and secret.
Imports and Setup
import datetime
import os
from zoneinfo import ZoneInfo
from fastapi import Depends, FastAPI, HTTPException, status, Request
from fastapi.responses import JSONResponse
from fastapi.security import HTTPBearer, HTTPAuthorizationCredentials
import jwt
import requests
from jwt.algorithms import RSAAlgorithm
from starlette.applications import Starlette
from starlette.routing import Route, Mount
import logging
from mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCP
from mcp.server.sse import SseServerTransport
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
FastAPI / Starlette: Provide the ASGI framework and request/response tools.
jwt & RSAAlgorithm: For decoding and verifying JWTs signed with RS256.
HTTPBearer: A security utility to parse
Authorization: Bearer <token>headers.dotenv: Loads environment variables (e.g., API keys).
logging: For server-side logging.
MCP modules:
FastMCPandSseServerTransportenable MCP over SSE.
Auth0 Configuration
AUTH0_DOMAIN = "zahere-dev.us.auth0.com"
API_AUDIENCE = "https://zahere-dev.us.auth0.com/api/v2/"
ALGORITHMS = ["RS256"]
# Set up logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger("mcp-server")
# Fetch JWKS keys once at startup
jwks_url = f"https://{AUTH0_DOMAIN}/.well-known/jwks.json"
jwks = requests.get(jwks_url, verify=False).json()
AUTH0_DOMAIN: Your Auth0 tenant domain.
API_AUDIENCE: The intended audience claim of the JWT (ensures tokens are meant for your API).
ALGORITHMS: We only accept
RS256(RSA signature with SHA-256).JWKS Fetch: At startup, the server downloads Auth0’s public signing keys. These are later used to validate incoming tokens.
JWT Verification Logic
# Auth setup
security = HTTPBearer()
def verify_jwt(token: str):
try:
header = jwt.get_unverified_header(token)
kid = header["kid"]
# Find matching JWK
key = next((k for k in jwks["keys"] if k["kid"] == kid), None)
if not key:
raise HTTPException(status_code=401, detail="Invalid auth key")
public_key = RSAAlgorithm.from_jwk(key)
payload = jwt.decode(
token,
public_key,
algorithms=ALGORITHMS,
audience=API_AUDIENCE,
issuer=f"https://{AUTH0_DOMAIN}/"
)
return payload
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"JWT validation error: {str(e)}")
raise HTTPException(status_code=401, detail="Invalid or expired token")
Extract header & KID: Each JWT contains a
kid(key ID). This tells us which public key was used to sign it.Find JWK: Match the
kidagainst Auth0’s JWKS set.RSAAlgorithm.from_jwk: Convert the JWK to a usable RSA public key.
jwt.decode: Validate the token signature, audience, issuer, and expiry.
If anything fails, raise a 401 Unauthorized error.
MCP Server & Tools (Minimal)
# ======================
# MCP Server Setup
# ======================
mcp = FastMCP(name="Weather and Time SSE Server")
@mcp.tool()
def TimeTool(input_timezone: str = None):
current_time = datetime.datetime.now()
if input_timezone:
current_time = current_time.astimezone(ZoneInfo(input_timezone))
return f"The current time is {current_time}."
transport = SseServerTransport("/messages/")
@mcp.tool()
def weather_tool(location: str):
api_key = os.getenv("OPENWEATHERMAP_API_KEY")
url = f"http://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather?q={location}&appid={api_key}&units=metric"
response = requests.get(url)
data = response.json()
if data.get("cod") == 200:
temp = data["main"]["temp"]
description = data["weather"][0]["description"]
return f"The weather in {location} is {description} with {temp}°C."
return f"Couldn't fetch weather for {location}."
A simple implementation of the MCP server tools
FastAPI App & Endpoints
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/sse")
async def handle_sse(request: Request):
auth_hdr = request.headers.get("authorization")
token = None
if auth_hdr and auth_hdr.lower().startswith("bearer "):
token = auth_hdr.split(" ", 1)[1]
else:
token = request.query_params.get("access_token")
if not token:
raise HTTPException(status_code=401, detail="Missing token")
verify_jwt(token)
async with transport.connect_sse(request.scope, request.receive, request._send) as (in_stream, out_stream):
await mcp._mcp_server.run(in_stream, out_stream, mcp._mcp_server.create_initialization_options())
Supports two auth methods:
Standard
Authorization: Bearer <token>header.Query parameter
?access_token=...(useful for browserEventSource).
Token is verified, then SSE connection is established.
Protecting the ASGI Transport
def auth_asgi_wrapper(asgi_app):
async def app(scope, receive, send):
if scope["type"] == "http":
headers = {k.decode().lower(): v.decode() for k, v in scope.get("headers", [])}
auth_hdr = headers.get("authorization")
if not auth_hdr or not auth_hdr.lower().startswith("bearer "):
resp = JSONResponse({"detail": "Not authenticated"}, status_code=401)
await resp(scope, receive, send)
return
token = auth_hdr.split(" ", 1)[1]
try:
verify_jwt(token)
except HTTPException as he:
resp = JSONResponse({"detail": he.detail}, status_code=he.status_code)
await resp(scope, receive, send)
return
except Exception:
resp = JSONResponse({"detail": "Invalid or expired token"}, status_code=401)
await resp(scope, receive, send)
return
await asgi_app(scope, receive, send)
return app
This wrapper protects the
/messages/endpoint. It intercepts requests, checks for a Bearer token, and validates it before passing control to the MCP transport.
Mount Messages Route
app.mount("/messages/", auth_asgi_wrapper(transport.handle_post_message))
This makes sure POST requests to
/messages/are also protected by our wrapper
Run the Server
if __name__ == "__main__":
import uvicorn
uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=8100)
The Client
**Below is only part of the client code**. Full code is available in repo.
def get_token():
import http.client
conn = http.client.HTTPSConnection(os.getenv("AUTH0_DOMAIN"))
payload = {"client_id":os.getenv("CLIENT_ID"), "client_secret":os.getenv("CLIENT_SECRET"),"audience":os.getenv("AUTH_AUDIENCE"),"grant_type":"client_credentials"}
headers = { 'content-type': "application/json" }
conn.request("POST", "/oauth/token", json.dumps(payload), headers)
res = conn.getresponse()
data = json.loads(res.read())
return data["access_token"]
async def main(queries: list[str]):
sse_url = "http://localhost:8100/sse"
logger.info(f"Generating Bearer token for authentication")
auth_token = get_token()
#auth_token = "12124234"
logger.info(f"Token generated {auth_token[:20]} ")
headers = {"Authorization": f"Bearer {auth_token}"}
try:
logger.info("Connecting to MCP Server with token")
# 1) Open SSE → yields (in_stream, out_stream)
async with sse_client(url=sse_url, headers=headers) as (in_stream, out_stream):
# 2) Create an MCP session over those streams
logger.info("Connected to MCP Server")
async with ClientSession(in_stream, out_stream) as session:
# 3) Initialize
info = await session.initialize()
logger.info(f"Connected to {info.serverInfo.name} v{info.serverInfo.version}")
# 4) List tools
tools = (await session.list_tools())
logger.info(tools)
### Run the queries
for query in queries:
prompt = get_prompt_to_identify_tool_and_arguements(query,tools)
logger.info(f"Printing Prompt \n {prompt}")
response = llm_client(prompt)
print(response)
tool_call = json.loads(response)
result = await session.call_tool(tool_call["tool"], arguments=tool_call["arguments"])
logger.success(f"User query: {query}, Tool Response: {result.content[0].text}")
except httpx.HTTPStatusError as http_e:
logger.exception(f"HTTP Error: {http_e}")
except Exception as e:
logger.exception(f"Error: {e}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
queries = ["What is the time in Bengaluru?", "What is the weather like right now in Dubai?"]
asyncio.run(main(queries))
Use the client_id and secret to connect with Auth0 and request for access token
Send the token to the MCP Server as a header with “Authorization” key.
If connection is established, you will see the message below, else 401 Unauthorized error